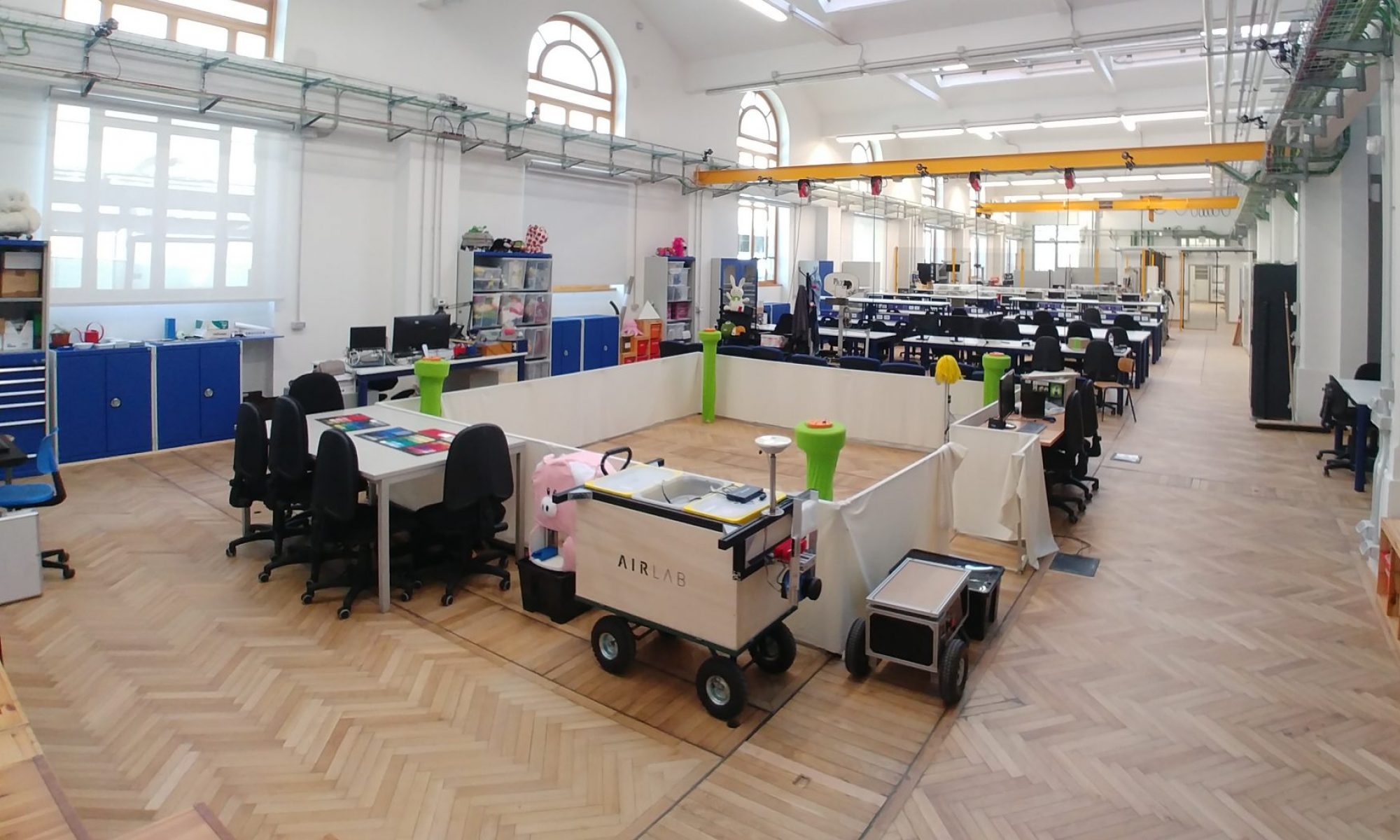
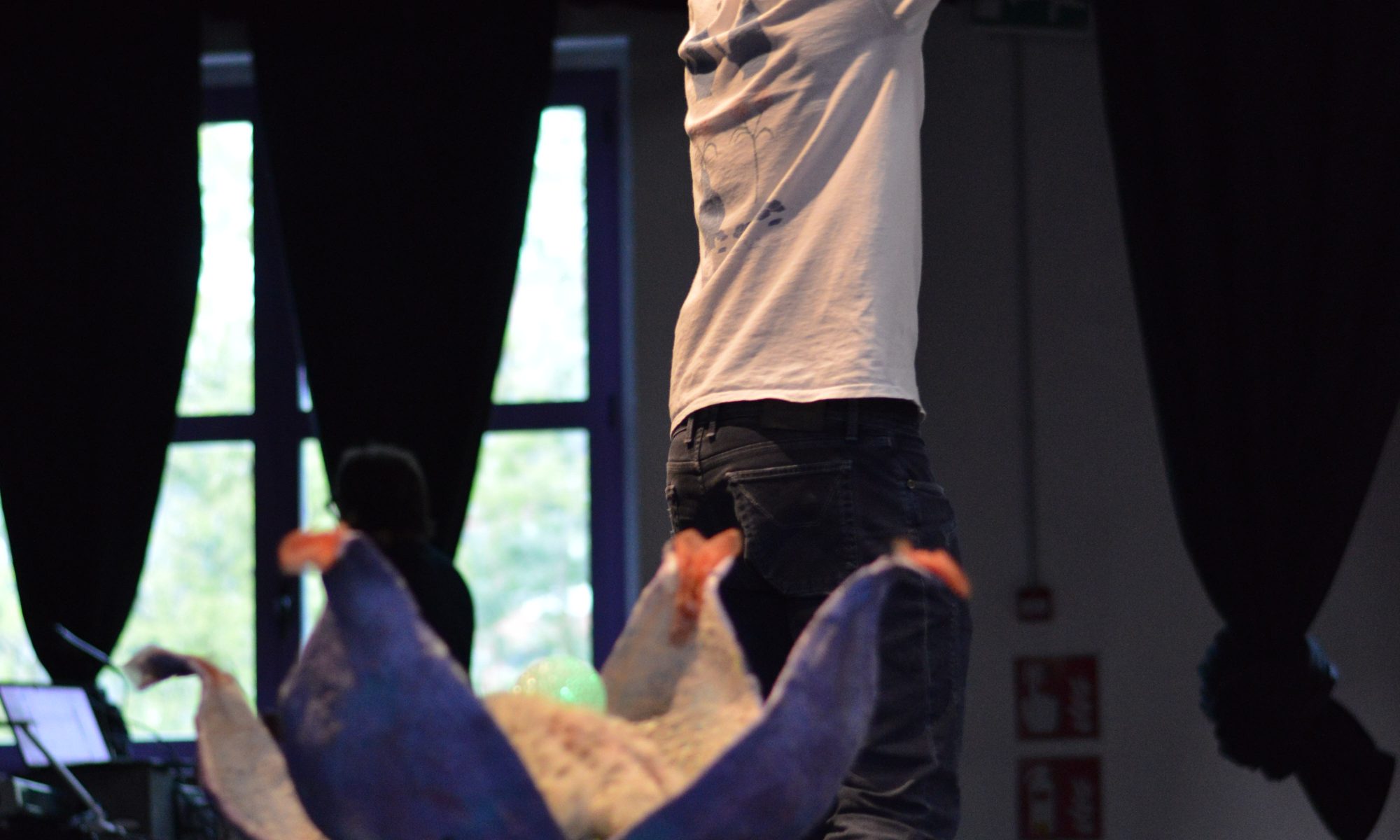
“First Contact” is a research project aimed at exploring embodiment and interaction with non-human entities, social robots and virtual shapes, through non-verbal communication, focusing on creating authentic, believable, and socially interactive characters. Subjects interact with each other through a digital filter that transforms their bodies into new creatures that the other will interact with, creating a context to test genuine understanding of this alien otherness.
The project follows two main tracks, “The Game” and “The Room”, experimenting with radically non-anthropomorphic bodies with different narratives and interaction contexts.
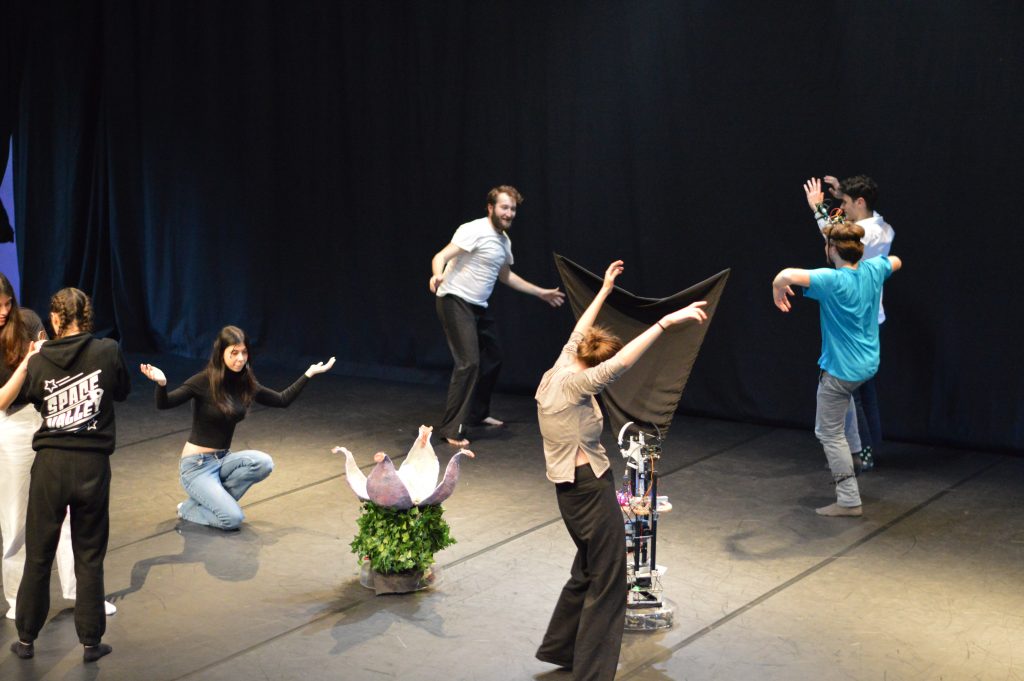

Hugh Herr believes that in the 21st century humans might extend their bodies into non- anthropomorphic forms, like wings, and control and feel these movements through their nervous system, drastically changing our morphology and dynamics. This concept raises questions about the nature of our bodies, identity, and potential virtual existences. Avatars are crucial in shaping our social lives and identities, as they become the means through which we embody and express ourselves.
It investigates the challenges of embodiment and genuine human interaction with non- anthropomorphic beings (in terms of shape, perception and expressive capabilities), using only non-verbal communication. By imbuing these entities with unique narratives, motivations, and desires, the study seeks to create truly authentic and relatable characters.
This research was introduced as the PhD of Federico Espositi and has developed into several multidisciplinary projects, from robot and interaction design, to the study of affordances in Virtual Reality, to the history of the concept itself of animacy and embodiment. Projects are higly experimental and often experiements take the shape of interactive installations or are inherently mixed with performance.
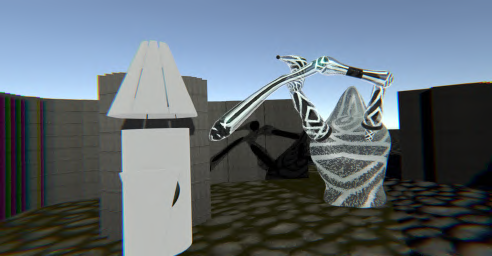
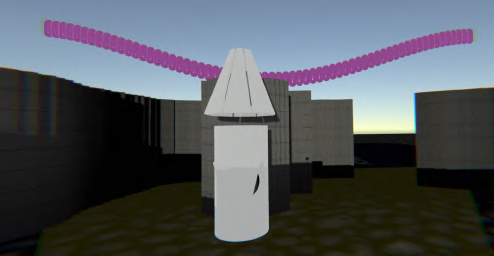

This study challenges traditional notions of what constitutes a living and social body, leveraging new technologies to expand our understanding of embodiment and cognition. As the concept of embodying avatars different from human morphology is gaining attention, this research investigates how far we can push the level of non-anthropomorphism while still retaining the possibility to understand the world and act in it through the avatar. Research on embodied cognition emphasizes the body’s central role in processing and understanding reality, while also showing the human’s capacity to re-adapt to different body morphologies, a phenomenon called homuncular flexibly. Thus, exploring radically altered bodies can help us surpass our current understanding of cognition.
At the same time, this research aims to determine what makes a non-human entity appear “alive” to humans by examining the physical elements, movements, sounds, and actions that contribute to this perception. This aim is shared with social psychology research, such as the famous Heider and Simmel test on social intelligence, where they showed that humans could attribute human-like behavior and motivations even to simple geometrical shapes, and the entire field of animation, starting from Disney’s “the illusion of life” showing the principles that could make a drawing of a half- empty sack of flour display emotions. Applications of this research range from social robotics to creating more relatable and empathetic characters in entertainment. The project aims at offering insights and guidelines into the development of realistic non-humanoid social creatures and their impact on human-technology engagement in an increasingly digital world.

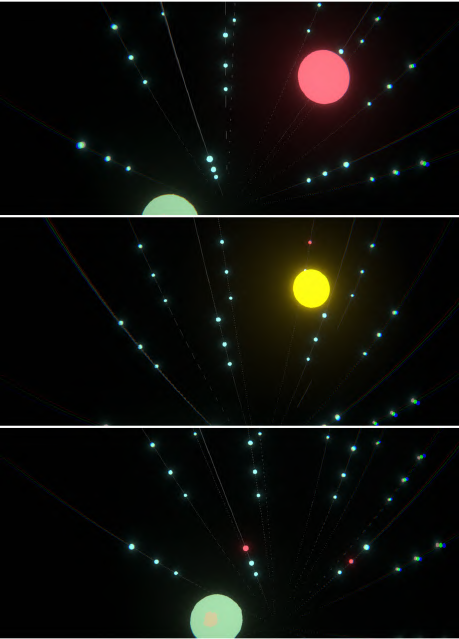
The Digital Filter
Both projects depend on a ‘digital filter’ — a mechanism that allows participants to interact while concealing their identities. One human acts as the Controller. The other human acts as ‘the Visitor’. The Controller embodies the avatar and controls the avatar by using embodied controllers. The Controller perceives reality in an altered way with a VR headset. The visual information the Controller perceives is a translation of data received by the avatar’s sensors in real-time. The representations the Controller sees are abstract. The human Visitor seen by the Controller is not a recognizable human entity. Meanwhile, the Visitor interacts with this non- anthropomorphic avatar.
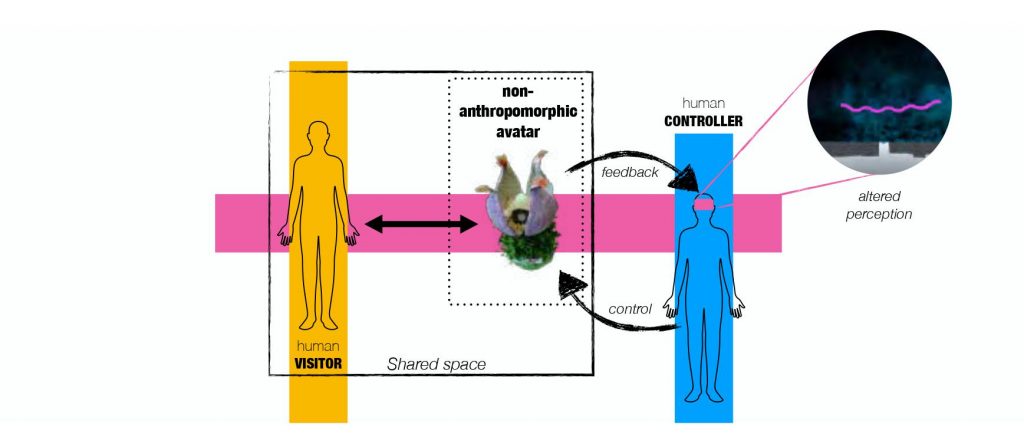
These two entities, Controller and Visitor, are in direct interaction within the same shared space, but act through the digital filter described above. Crucially, the two can’t speak. They can only communicate through the motion of their digitally filtered bodies. Neither is able to perceive another human directly. Instead, they are each ‘the other’ human ‘translated’ into an alien presence.
Both instances can be considered “first contact” between two beings that don’t know or understand each other at first, with non-anthropomorphic bodies, that need to find a way to learn how to communicate non-verbally to achieve some sort of objective.
Pilot
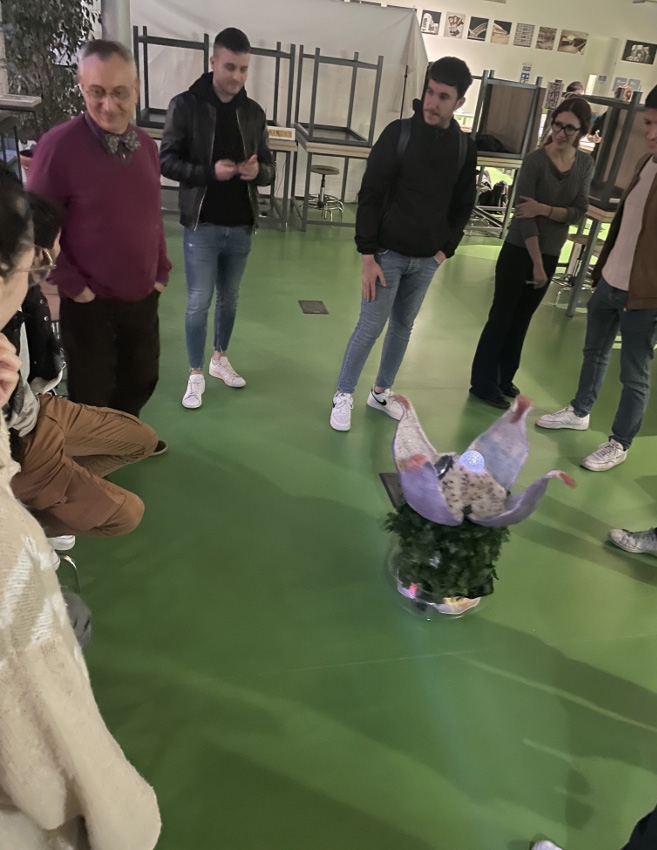



This first prototype of the entire system gave rise to an initial overall conceptual
framework and has been refined and turned into an interactive installation, “Connect to the Machine”, and presented at the Milano Digital Week 2022. This art installation was instrumental for the testing of the system outside of the laboratory, with a variety of users, and feedback data was collected that drove the following steps of the research. The initial prototype, the framework and the art installation were the subjects of a paper published at the xCoAx conference on aesthetics and computation.
Read the paper here.
The Projects
The research is divided into two main projects, each an incarnation of the main setup: “The Game” and “The Room”. They all share objectives and methodologies, but based on each project’s main focus, there are slight variations.
The Game

The Controller and Visitor play a collaborative game. The Visitor interacts with a mobile robot in the real world while the Controller plays a game in VR, unknowingly controlling the robot in the physical space in real time. They both find themselves in a maze, and they have to escape it in a short time.
Either one is privy to information that the other requires, but only the other player can actually perform actions required to win. To each user, the other is an unfamiliar alien. Moreover, the two cannot speak: they must communicate non-verbally, and they will need to learn how to cooperate to escape. With this project we push the boundaries of communication, driving the users to the extreme with a time limit objective.
More on the Game track here.
The Room

The Visitor enters a closed space, a room, and finds it to be an entire abstract living organism. A space that has come to life. This space is none other than the avatar that the Controller is embodying. This research pushes the boundaries of interaction itself. Notions of gaze, body, personal distance, attention, they are all disrupted, as these two beings find themselves one inside the other. What kind of interaction is possible in such a condition? How can a space be alive?
More on the Room track here.
Spin Off Projects
Beyond the two main tracks, spin-off projects that are objective-oriented address a subset of the topics of the main research.
Raw Machines
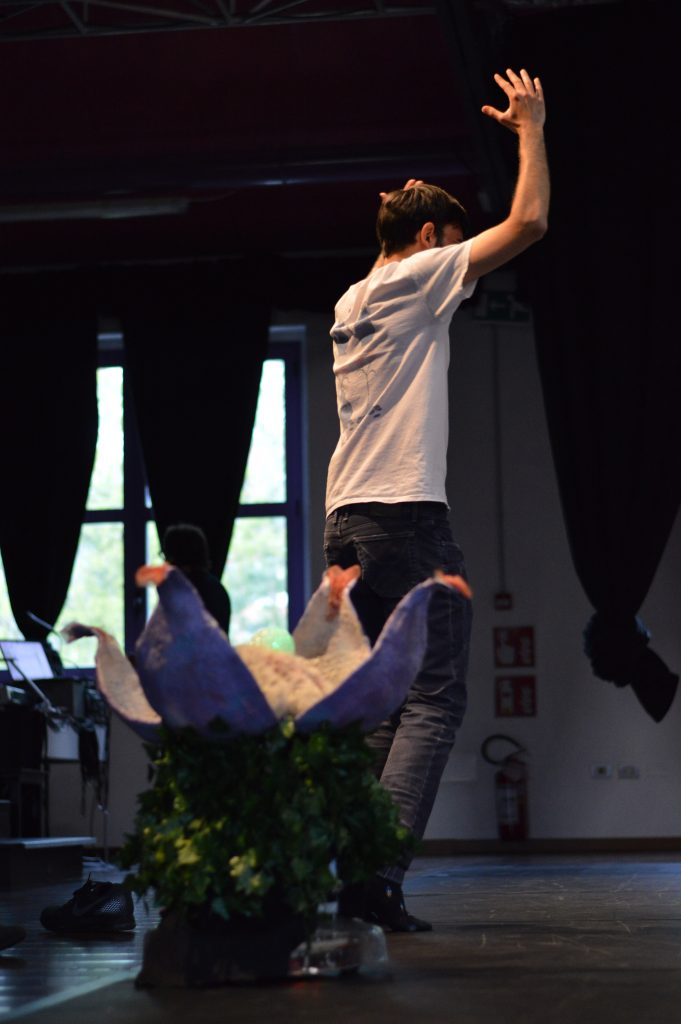

“Raw Machines” was born as a device for a workshop merging physical theatre and robotics. Taking place in a theatrical space, participants control non-humanoid social robots via wearable devices and wireless systems, promoting flexibility and creative experimentation. The workshop enhances body awareness and non-verbal communication, transcending cultural barriers. It fosters digital literacy by demystifying technology components. Led by a myself and a professional dancer, it culminates in group performances. Aims of this project are to foster digital literacy reaching a broad and diverse audience, and push the boundaries of the expressive potentials of the developed robot bodies.
Read the paper here.
People

Project by:
Federico Espositi. federico.espositi@polimi.it
Supervision:
Andrea Bonarini. andrea.bonarini@polimi.it
Our students:
Thesis
Erica Panelli. Computer Science
Giulia Carri. Computer Science
Giuseppe Epifani. Computer Science
Maurizio Vetere. Computer Science
Amor Madhkour. Computer Science
Francesco Calabrese. Computer Science
Zeynep Erol. Digital Interaction Design
Sobhan Esfandiar. Design Engineering
Giuseppe Bonanno. Computer Science
Giovanni Sassone Massari. Product Design
Davide Maria Cardillo. Automation&Control Engineering
Andrea Gerosa. Computer Science

